Complete the sentences describing neuroglia cells – Neuroglia cells, the unsung heroes of the nervous system, play a pivotal role in maintaining its delicate balance. Delve into their world as we unravel their diverse functions, from providing structural support to safeguarding the brain’s integrity. This comprehensive exploration of neuroglia cells promises to shed light on their multifaceted nature and their profound impact on our cognitive well-being.
As we delve deeper into the realm of neuroglia cells, we will discover their remarkable diversity, ranging from the star-shaped astrocytes to the enigmatic microglia. Each type possesses unique characteristics and responsibilities, contributing to the harmonious functioning of the nervous system.
Moreover, we will explore the intricate relationship between neuroglia cells and neurodegenerative diseases, uncovering their potential role in the development and progression of conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Neuroglia Cells: Complete The Sentences Describing Neuroglia Cells
Neuroglia cells, also known as glial cells, are non-neuronal cells that make up the supportive tissue of the nervous system. They outnumber neurons by 10 to 1 and play a crucial role in maintaining the health and proper functioning of the nervous system.
Types of Neuroglia Cells
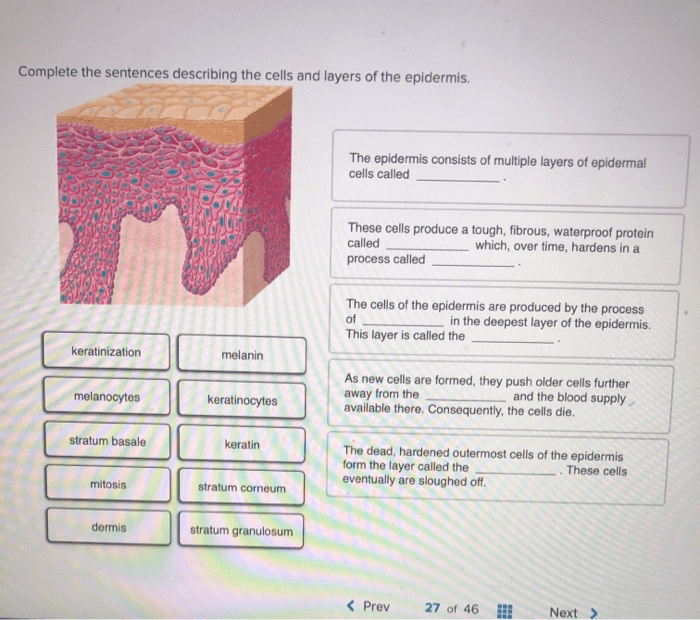
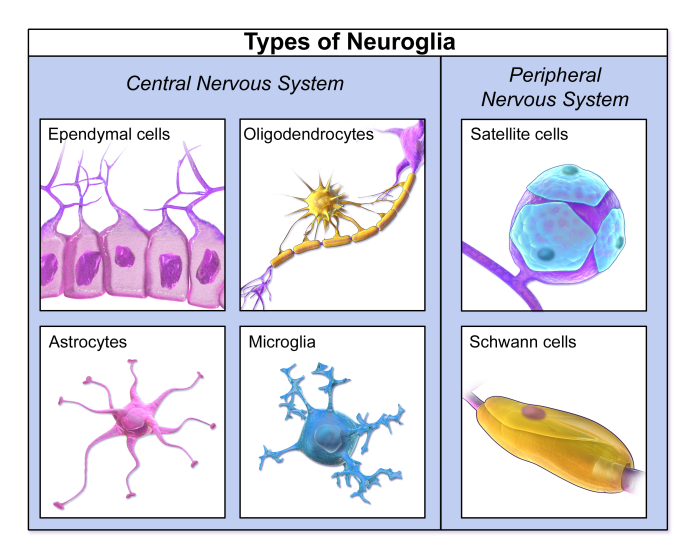
There are several types of neuroglia cells, each with specific functions and locations:
- Astrocytes:Star-shaped cells that provide structural support, regulate the chemical environment around neurons, and form the blood-brain barrier.
- Oligodendrocytes:Cells that produce myelin, a fatty substance that insulates axons and speeds up nerve impulses.
- Schwann cells:Similar to oligodendrocytes, they produce myelin but are found in the peripheral nervous system.
- Microglia:Small, motile cells that act as the immune cells of the nervous system, removing debris and pathogens.
- Ependymal cells:Cells that line the ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord, producing cerebrospinal fluid.
Functions of Neuroglia Cells

Neuroglia cells perform a wide range of protective and supportive functions:
- Physical support:They provide structural scaffolding for neurons and blood vessels.
- Metabolic support:They supply nutrients to neurons and remove waste products.
- Electrical insulation:Myelin produced by oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells insulates axons, preventing electrical impulses from leaking out.
- Homeostasis:Astrocytes regulate the chemical environment around neurons, maintaining ion balance and pH levels.
- Repair:Microglia remove damaged neurons and debris, while astrocytes form scar tissue to protect injured areas.
Neuroglia Cells and the Blood-Brain Barrier
Astrocytes play a crucial role in forming the blood-brain barrier (BBB), a protective layer that prevents harmful substances from entering the brain. The BBB consists of tight junctions between astrocytes and endothelial cells that line blood vessels in the brain.
This barrier is essential for maintaining the brain’s unique chemical environment and protecting it from toxins, pathogens, and other potentially damaging substances.
Neuroglia Cells and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Dysfunction of neuroglia cells has been implicated in several neurodegenerative diseases:
- Alzheimer’s disease:Astrocytes and microglia are involved in the formation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, characteristic of the disease.
- Parkinson’s disease:Microglia may contribute to the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra.
Understanding the role of neuroglia cells in these diseases could lead to new therapeutic approaches for neurodegenerative disorders.
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary function of neuroglia cells?
Neuroglia cells provide structural support, regulate homeostasis, and protect the nervous system from damage.
How do neuroglia cells contribute to the blood-brain barrier?
Neuroglia cells form tight junctions that prevent harmful substances from entering the brain.
What is the role of neuroglia cells in neurodegenerative diseases?
Dysfunction of neuroglia cells has been implicated in the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.