Conduit dies cut a taper of, a technique that combines the precision of die cutting with the versatility of tapering, opens up a world of possibilities for custom solutions across various industries. This innovative approach enables the creation of conduits that meet specific requirements, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Die cutting, a process that utilizes sharp blades to cut materials into precise shapes, and tapering, the gradual reduction of a material’s thickness, are seamlessly integrated to produce conduits that cater to unique applications. This combination offers a wide range of benefits, including improved cable management, enhanced protection against environmental factors, and reduced installation time.
Conduits
Conduits are hollow pipes or tubes designed to protect and route electrical wires, cables, and other utilities. They provide a safe and organized path for these essential components, ensuring proper functioning and preventing damage or accidents.
Materials Used
- Metal Conduits:Steel, aluminum, and stainless steel conduits offer high durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion. They are commonly used in industrial and commercial settings.
- Non-Metallic Conduits:PVC (polyvinyl chloride), CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride), and fiberglass conduits are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to chemicals and moisture. They are often used in residential and commercial buildings.
- Flexible Conduits:Liquid-tight, metallic, and non-metallic flexible conduits provide protection in areas with limited space or frequent movement. They are used in industrial machinery, automotive applications, and robotics.
Industries
- Construction:Conduits are essential in electrical installations, wiring systems, and utility distribution.
- Industrial:Conduits protect wires and cables in manufacturing facilities, power plants, and other industrial environments.
- Commercial:Conduits ensure safe and efficient wiring in offices, retail stores, and public buildings.
- Telecommunications:Conduits provide a secure path for fiber optic cables and other telecommunication infrastructure.
Die Cutting
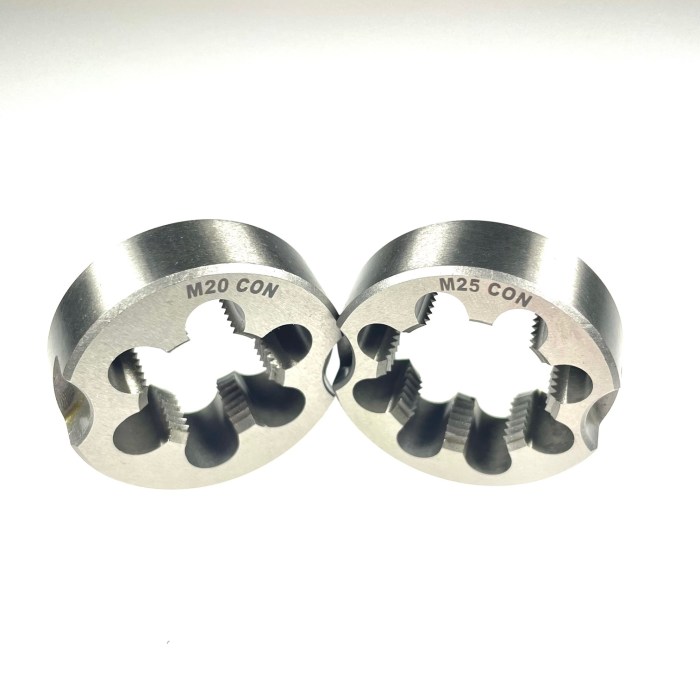

Die cutting is a process that uses sharp metal dies to cut various materials into specific shapes and sizes. It involves applying pressure to the die, which cuts through the material being processed.
Die-cutting machines come in different types, including manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic machines. Manual machines require manual operation, while semi-automatic machines offer some automation features. Fully automatic machines are highly automated, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Materials for Die Cutting
Die cutting can be used with a wide range of materials, including:
- Paper and cardboard
- Plastic
- Fabric
- Leather
- Rubber
- Foam
li>Metal
Tapering
Tapering involves gradually reducing the thickness or diameter of a material along its length. This process serves various purposes, including enhancing structural stability, improving load distribution, and facilitating assembly or insertion into tight spaces.
Methods of Tapering
Different methods are employed for tapering materials, each suited to specific applications:
- Mechanical Tapering:Uses cutting tools, such as lathes or milling machines, to remove material and create a tapered shape.
- Thermal Tapering:Involves heating the material and then applying pressure to induce deformation and create a tapered form.
- Chemical Tapering:Employs chemical etching or electrochemical machining to selectively remove material and achieve the desired taper.
Applications of Tapering
Tapering finds applications in various industries:
- Automotive:Tapered shafts and axles transmit power and reduce stress concentrations.
- Aerospace:Tapered wings improve aerodynamic efficiency and stability.
- Construction:Tapered columns and beams distribute loads more effectively.
- Medical:Tapered implants and surgical instruments facilitate insertion and reduce tissue damage.
Combining Conduit, Die Cutting, and Tapering
Combining conduits, die cutting, and tapering techniques offers a versatile approach to creating customized solutions for various industries. By integrating these processes, manufacturers can produce conduits tailored to specific requirements, optimizing performance and efficiency.
Die cutting involves using specialized tools to precisely shape and cut materials, while tapering refers to the process of gradually reducing the diameter or thickness of a material. When combined with conduits, these techniques enable the creation of conduits with specific geometries, dimensions, and tapers, meeting the unique needs of different applications.
Industries Benefiting from Combined Conduit, Die Cutting, and Tapering
Numerous industries benefit from the combination of conduit, die cutting, and tapering, including:
- Automotive:Custom-shaped conduits are used in vehicle wiring harnesses to optimize space utilization and improve signal transmission.
- Medical:Tapered conduits facilitate the insertion of medical devices into the body, ensuring precise placement and minimizing tissue damage.
- Telecommunications:Die-cut conduits enable the creation of complex cable management systems, enhancing signal integrity and reducing interference.
Case Studies Demonstrating Effectiveness
The following case studies illustrate the effectiveness of combining conduit, die cutting, and tapering:
- Automotive Wiring Harness Optimization:A leading automotive manufacturer partnered with a conduit supplier to develop custom die-cut conduits with tapered ends. This solution reduced harness weight by 20%, improved signal transmission, and simplified assembly.
- Medical Device Insertion:A medical device company utilized tapered conduits to enhance the insertion of a new surgical instrument. The gradual reduction in diameter allowed for precise placement and minimized patient discomfort.
- Telecommunications Cable Management:A telecommunications provider implemented die-cut conduits to create a customized cable management system for a high-density data center. The solution optimized airflow, reduced cable clutter, and improved network performance.
Design Considerations

When designing conduits for die cutting and tapering, it’s crucial to consider several factors. These factors influence the material selection, techniques employed, and ultimately the performance and longevity of the conduits.
Material Selection, Conduit dies cut a taper of
The choice of materials for conduits intended for die cutting and tapering is critical. The material must possess certain properties to withstand the stresses and deformations involved in these processes. Some key considerations include:
- Flexibility:The material should be pliable enough to allow for bending and shaping without cracking or breaking.
- Strength:The conduit must be strong enough to resist tearing or puncturing during die cutting and tapering.
li> Corrosion Resistance:The material should be resistant to corrosion, especially if the conduits are exposed to harsh environments.
Die Cutting and Tapering Techniques
The techniques used for die cutting and tapering conduits vary depending on the material and the desired shape. Some common techniques include:
- Rotary Die Cutting:This technique uses a rotating die to cut the conduit material into the desired shape.
- Laser Cutting:Laser cutting uses a focused laser beam to precisely cut the conduit material.
- Waterjet Cutting:Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure water jet to cut the conduit material.
Performance and Longevity
Optimizing the performance and longevity of conduits subjected to die cutting and tapering requires attention to several factors:
- Design:Proper design considerations, including material selection and technique selection, are essential for ensuring optimal performance.
- Manufacturing:Precise manufacturing techniques and quality control measures help ensure the conduits meet the required specifications.
- Installation:Proper installation practices, including correct handling and support, contribute to the conduit’s longevity.
Industry Applications
Conduits that have undergone die-cutting and tapering find applications in diverse industries, each presenting unique requirements and challenges.
Across these industries, these conduits offer advantages such as improved cable management, reduced installation time, and enhanced protection for sensitive cables.
Electrical and Construction
In electrical and construction projects, conduits play a crucial role in organizing and protecting electrical wiring systems. Die-cut and tapered conduits facilitate easier cable routing, especially in tight spaces or when navigating obstacles.
The tapered design enables smooth cable insertion and reduces the risk of damage during installation, ensuring reliable electrical connections and system longevity.
Automotive
Within the automotive industry, conduits are essential for managing electrical wiring harnesses and protecting them from harsh environmental conditions. Die-cut and tapered conduits offer flexibility and durability, allowing for efficient cable routing and protection in confined spaces.
The customizability of these conduits allows for tailored solutions to meet specific vehicle requirements, enhancing safety and reliability.
Aerospace
In the aerospace sector, conduits are vital for managing critical electrical systems and ensuring aircraft safety. Die-cut and tapered conduits provide lightweight and compact solutions for routing cables in complex aircraft structures.
The ability to customize the shape and size of these conduits enables precise cable management, reducing weight and improving overall aircraft performance.
Medical
Within the medical field, conduits play a significant role in delivering medical gases and fluids safely and efficiently. Die-cut and tapered conduits facilitate precise and secure connections, ensuring accurate delivery of critical substances.
The tapered design allows for easy insertion of medical devices and minimizes the risk of leaks or contamination, enhancing patient safety and treatment outcomes.
When conduit dies cut a taper of 30 degrees, it creates a funnel-shaped end that can be easily inserted into a pipe or fitting. For more information on biomes, check out this biomes of North America PDF . Conduit dies are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, so you can find the right one for your project.
Advanced Techniques

The production of conduits often requires the use of advanced techniques to achieve the desired shape, size, and functionality. Die cutting and tapering are two essential techniques that are commonly employed in this process. These techniques involve the use of specialized machinery and tooling to cut and shape the conduit material precisely.
Benefits of Advanced Techniques
Advanced techniques offer several benefits in the production of conduits:
- Precision:Die cutting and tapering techniques allow for highly precise cutting and shaping of the conduit material, ensuring consistent dimensions and tolerances.
- Efficiency:These techniques enable efficient production of conduits in high volumes, reducing labor costs and production time.
- Versatility:Advanced techniques can be used to produce conduits of various shapes, sizes, and materials, meeting diverse application requirements.
Limitations of Advanced Techniques
While advanced techniques offer significant benefits, they also have certain limitations:
- Cost:Die cutting and tapering machinery and tooling can be expensive, making these techniques less accessible for small-scale production.
- Complexity:These techniques require specialized knowledge and expertise to operate the machinery and ensure proper setup and maintenance.
- Material constraints:Not all conduit materials are suitable for die cutting and tapering, and certain materials may require specialized tooling or modifications.
Emerging Technologies
The field of conduit production is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging to enhance efficiency, precision, and versatility. Some promising emerging technologies include:
- Laser cutting:Laser cutting technology offers precise and intricate cutting of conduit materials, enabling complex shapes and designs.
- Waterjet cutting:Waterjet cutting utilizes a high-pressure water stream to cut through conduit materials, providing a burr-free and clean finish.
- 3D printing:3D printing technology allows for the production of custom-shaped conduits with complex geometries, reducing the need for traditional die cutting and tapering.
Quality Control

Quality control is paramount in the production of conduits that undergo die cutting and tapering. Ensuring the integrity and reliability of these conduits is crucial for their intended applications.
Inspection and Testing
Rigorous inspection and testing measures are essential to verify the quality of conduits. These include:
- Dimensional Accuracy:Conduits must meet precise dimensional specifications to ensure proper fit and functionality.
- Taper Consistency:The taper of conduits should be uniform and within specified tolerances to facilitate smooth insertion and prevent leaks.
- Material Integrity:Conduits should be made of high-quality materials that can withstand the rigors of their intended environment.
- Performance Testing:Conduits are subjected to various performance tests, such as pressure testing, to ensure they meet the required standards.
Best Practices
To ensure the consistency and reliability of conduits, best practices include:
- Established Standards:Adhering to industry standards and specifications provides a benchmark for quality.
- Process Control:Implementing rigorous process controls helps minimize variations and maintain consistency.
- Continuous Improvement:Regularly reviewing and improving quality control measures ensures ongoing optimization.
- Training and Certification:Training and certifying personnel involved in the production process ensures proficiency and adherence to standards.
Sustainability
The production of conduits through die cutting and tapering processes raises environmental concerns due to the use of raw materials and the generation of waste. Understanding the impact and adopting sustainable practices is crucial for minimizing the ecological footprint.
Sustainable practices in conduit production involve reducing waste, optimizing material usage, and adopting energy-efficient technologies. This can be achieved through measures such as:
Waste Reduction
- Implementing efficient cutting techniques to minimize material wastage.
- Recycling scrap material and using it for other purposes.
- Exploring alternative materials with lower environmental impact.
Energy Optimization
- Utilizing energy-efficient machinery and equipment.
- Optimizing production processes to reduce energy consumption.
- Exploring renewable energy sources for powering production facilities.
Case Study
Company X, a leading manufacturer of conduits, has implemented a comprehensive sustainability program that includes:
- Investment in state-of-the-art die cutting equipment that reduces waste by 20%.
- Establishment of a recycling program for scrap materials, diverting 80% from landfills.
- Adoption of solar energy to power a portion of its manufacturing facility.
Through these initiatives, Company X has significantly reduced its environmental impact and set an example for the industry.
Future Trends
The conduit industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging all the time. Die cutting and tapering are two important processes that are used in the production of conduits, and they are likely to continue to play a vital role in the future.
One of the most important trends in the conduit industry is the increasing use of automation. This is being driven by the need to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Automated die cutting and tapering machines can produce conduits more quickly and accurately than manual machines, and they can also be used to produce more complex shapes.
Potential Growth Areas
There are a number of potential growth areas for the conduit industry in the future. One area is the use of conduits in renewable energy applications. Conduits are used to protect electrical cables in solar and wind farms, and the demand for these conduits is expected to grow as the use of renewable energy increases.
Another potential growth area is the use of conduits in data centers. Data centers are used to store and process large amounts of data, and they require a reliable and efficient way to manage their electrical cables. Conduits can help to protect these cables from damage and interference, and they can also be used to organize and route them.
Innovation Opportunities
There are a number of opportunities for innovation in the conduit industry. One area is the development of new materials for conduits. Traditional materials such as steel and aluminum are still widely used, but there is a growing demand for lighter and more durable materials.
New materials such as composites and polymers are being developed to meet this demand.
Another area of innovation is the development of new die cutting and tapering technologies. These technologies can be used to produce more complex shapes and to improve the efficiency of the production process. New technologies such as laser cutting and waterjet cutting are being developed to meet this demand.
FAQ Compilation: Conduit Dies Cut A Taper Of
What are the advantages of using conduit dies cut a taper of?
Conduit dies cut a taper of offer several advantages, including precise shape cutting, reduced installation time, enhanced protection against environmental factors, and custom solutions tailored to specific requirements.
How does the process of conduit dies cut a taper of work?
Conduit dies cut a taper of involves using sharp blades to cut materials into precise shapes, followed by tapering, which gradually reduces the material’s thickness. This combination allows for the creation of custom conduits that meet specific design requirements.
What industries commonly utilize conduit dies cut a taper of?
Conduit dies cut a taper of find applications in various industries, including electrical, automotive, telecommunications, and construction, where custom solutions are required to meet specific performance and installation needs.