Comparative constitutions answer key PDF unlocks the gateway to understanding constitutional systems worldwide. This comprehensive resource delves into the intricacies of comparative constitutional analysis, illuminating the key elements of constitutions, exploring comparative case studies, and unraveling the fundamental principles that shape constitutional interpretation.
Get ready to embark on a journey that will deepen your comprehension of constitutional law and comparative jurisprudence.
Comparative constitutional analysis provides a unique lens through which to examine different constitutional systems, revealing their similarities, differences, and the underlying principles that guide their interpretation and application. This in-depth analysis empowers scholars, legal practitioners, and policymakers to draw informed comparisons, identify best practices, and contribute to the ongoing evolution of constitutional law.
Comparative Constitutional Analysis
Comparative constitutional analysis is a field of study that examines and compares different constitutional systems. It seeks to understand the similarities and differences between constitutions, identify common patterns and principles, and explore the ways in which constitutional law shapes political systems and societies.
Key Concepts of Comparative Constitutional Analysis, Comparative constitutions answer key pdf
- Comparative method: Involves comparing two or more constitutions to identify similarities, differences, and patterns.
- Constitutionalism: The belief that government power should be limited and constrained by a written constitution.
- Rule of law: The principle that all persons, including government officials, are subject to and accountable under the law.
- Separation of powers: The division of government power among different branches to prevent tyranny.
- Judicial review: The power of courts to review and invalidate laws that violate the constitution.
Examples of Comparative Constitutional Analysis
- Comparing the constitutions of the United States and Canada to understand different approaches to federalism.
- Examining the constitutions of South Africa and India to analyze the role of constitutional courts in protecting human rights.
- Studying the constitutions of China and Russia to explore different models of constitutionalism in authoritarian regimes.
Advantages and Limitations of Comparative Constitutional Analysis
Advantages
- Provides a broader understanding of constitutional systems and principles.
- Identifies best practices and lessons learned from different constitutional models.
- Facilitates constitutional reform and development.
Limitations
- Can be challenging to compare constitutions from different cultural and historical contexts.
- May oversimplify complex constitutional issues.
- Can lead to cherry-picking of examples to support particular arguments.
Key Elements of Constitutions

Most constitutions share certain common elements, including:
Preamble
A statement of the constitution’s purpose, principles, and values.
Bill of Rights
A list of fundamental rights and freedoms guaranteed to individuals.
Structure of Government
Describes the branches of government, their powers, and relationships.
Amendment Process
The procedure for changing the constitution.
Variations in Constitutional Elements
While these elements are common, their specific content and interpretation can vary significantly across different constitutions. For example:
- The Bill of Rights in the US Constitution is more extensive than in many other constitutions.
- The structure of government in the UK is based on a parliamentary system, while the US has a presidential system.
- The amendment process in the US is more difficult than in many other countries.
Comparative Case Studies

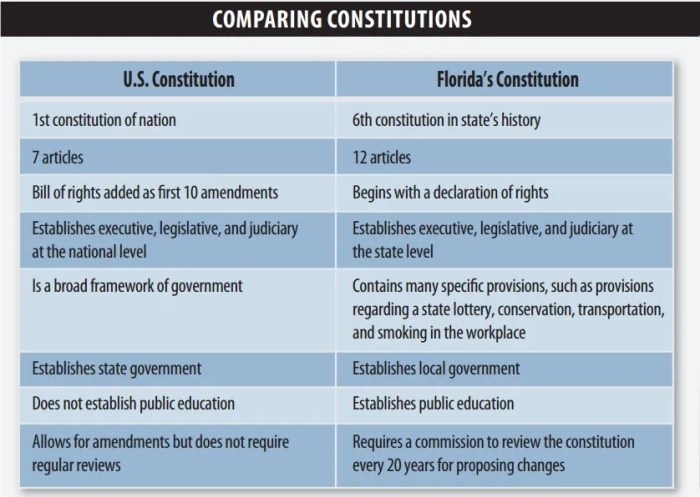
Table Comparing Constitutions of the United States and Canada
| Feature | United States | Canada |
|---|---|---|
| Federalism | Strong federal government with limited state powers | Weaker federal government with more provincial autonomy |
| Bill of Rights | Extensive Bill of Rights in the Constitution | Charter of Rights and Freedoms enacted separately |
| Judicial Review | Supreme Court has power of judicial review | Supreme Court has limited power of judicial review |
Comparative Constitutional Principles
Fundamental Principles
- Popular sovereignty
- Limited government
- Separation of powers
- Rule of law
- Protection of individual rights
Interpretation and Application
These principles are interpreted and applied differently in different constitutional systems. For example:
- The US Constitution is interpreted more strictly than the Canadian Constitution.
- The principle of separation of powers is more strictly enforced in the US than in the UK.
- The protection of individual rights is stronger in some constitutions than in others.
Constitutional Interpretation: Comparative Constitutions Answer Key Pdf
Approaches to Interpretation
- Originalism: Focuses on the original intent of the constitution’s drafters.
- Living constitutionalism: Interprets the constitution as a living document that evolves over time.
- Purposivism: Focuses on the purpose and goals of the constitution.
Methods of Interpretation
- Textualism: Focuses on the plain meaning of the constitutional text.
- Structuralism: Examines the structure and organization of the constitution.
- Historical analysis: Considers the historical context in which the constitution was drafted.
Role of Judicial Review
Courts play a crucial role in interpreting constitutions through the process of judicial review. This involves reviewing laws and government actions to ensure they comply with the constitution.
Essential Questionnaire
What is comparative constitutional analysis?
Comparative constitutional analysis is a method of studying constitutions by comparing them to each other. This allows scholars to identify similarities and differences between constitutions, and to draw conclusions about the strengths and weaknesses of different constitutional systems.
What are the key elements of a constitution?
The key elements of a constitution typically include a statement of fundamental rights, a structure of government, and a process for amending the constitution.
What are some of the most important comparative constitutional principles?
Some of the most important comparative constitutional principles include the rule of law, the separation of powers, and the protection of fundamental rights.