Tragedy of the commons ap environmental science – The Tragedy of the Commons in Environmental Science sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This exploration delves into the complex dynamics of resource depletion and sustainability, examining the underlying causes and consequences of this pervasive issue.
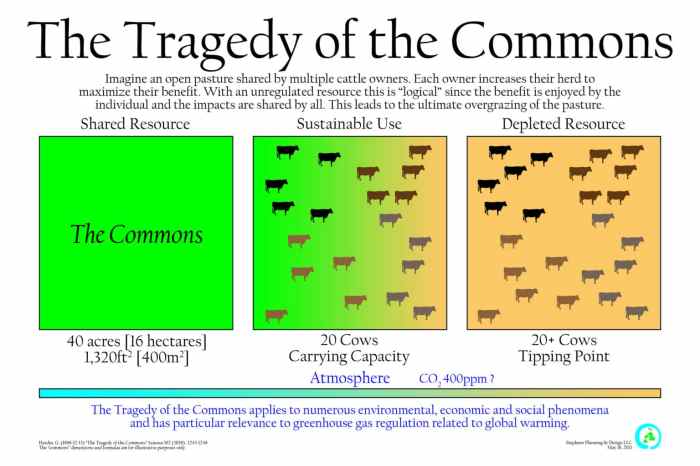
The concept of the tragedy of the commons revolves around the idea that individuals acting in their own self-interest can collectively deplete a shared resource, even if it is in their long-term best interest to conserve it. This phenomenon has been observed in various real-world scenarios, such as overgrazing of common pastures, overfishing of shared fishing grounds, and pollution of shared air and water resources.
Definition and Overview of the Tragedy of the Commons
The tragedy of the commons is a concept that describes a situation in which individuals or groups acting independently in their own self-interest collectively deplete or degrade a shared resource. This occurs when the benefits of exploiting the resource are immediate and private, while the costs are diffused and long-term.
Examples of the tragedy of the commons include:
- Overgrazing of communal pastures
- Overfishing of fisheries
- Pollution of air and water
The underlying causes of the tragedy of the commons include:
- Lack of clear property rights
- High costs of exclusion
- Large number of users
Consequences and Impacts of the Tragedy of the Commons
The consequences of the tragedy of the commons can be severe and include:
- Depletion of resources
- Environmental degradation
- Social conflict
The long-term effects of the tragedy of the commons can include:
- Loss of biodiversity
- Climate change
- Economic decline
Solutions and Strategies to Address the Tragedy of the Commons

Several approaches and strategies have been proposed to address the tragedy of the commons, including:
- Government regulations
- Economic incentives
- Education
The effectiveness of these solutions depends on the specific context and the nature of the resource being managed.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
The tragedy of the commons has been observed in many real-world situations, including:
- The Aral Sea
- The Grand Banks fishery
- The Amazon rainforest
These case studies provide valuable lessons about the factors that lead to the tragedy of the commons and the importance of finding effective solutions.
Policy Implications and Recommendations

The tragedy of the commons has important policy implications, including:
- The need for clear property rights
- The role of government in regulating the use of common resources
- The importance of education and awareness-raising
Policymakers, stakeholders, and the public all have a role to play in addressing the tragedy of the commons and promoting the sustainable use of shared resources.
Common Queries: Tragedy Of The Commons Ap Environmental Science
What is the tragedy of the commons?
The tragedy of the commons refers to the situation where individuals acting in their own self-interest deplete a shared resource, even if it is in their long-term best interest to conserve it.
What are some examples of the tragedy of the commons?
Examples of the tragedy of the commons include overgrazing of common pastures, overfishing of shared fishing grounds, and pollution of shared air and water resources.
What are the underlying causes of the tragedy of the commons?
The underlying causes of the tragedy of the commons include lack of clear property rights, high costs of exclusion, and the difficulty of monitoring and enforcing sustainable use of the resource.
What are some strategies to address the tragedy of the commons?
Strategies to address the tragedy of the commons include government regulations, economic incentives, and education to promote sustainable use of shared resources.