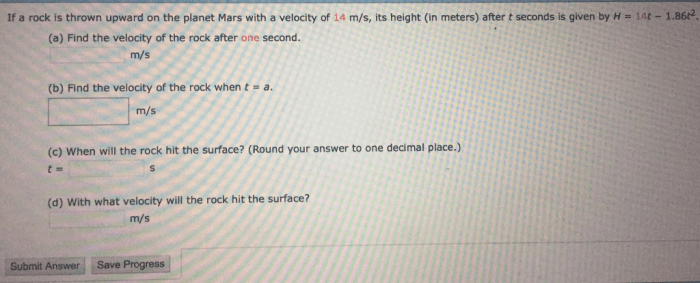
If a rock is thrown upward on the planet mars – When a rock is thrown upward on the planet Mars, its trajectory is influenced by a unique set of physical factors. This article delves into the intriguing dynamics of projectile motion on Mars, examining the interplay between gravity, atmospheric conditions, and the resulting trajectory of an upward-thrown rock.
The Martian atmosphere, with its distinct composition and density, plays a crucial role in shaping the trajectory of a projectile. Air resistance and wind patterns can significantly alter the path of an object thrown upward, leading to deviations from the parabolic trajectory observed on Earth.
Projectile Motion on Mars: If A Rock Is Thrown Upward On The Planet Mars

Projectile motion on Mars differs from Earth due to the planet’s lower gravity and thinner atmosphere. When an object is thrown upward on Mars, it experiences a smaller gravitational force and less air resistance compared to Earth.
The trajectory of a projectile on Mars is determined by its initial velocity, the Martian gravitational constant (3.71 m/s 2), and the Martian atmospheric conditions.
Mars’ Atmospheric Conditions, If a rock is thrown upward on the planet mars
The Martian atmosphere is composed primarily of carbon dioxide (95.3%), nitrogen (2.7%), and argon (1.6%). It is much thinner than Earth’s atmosphere, with a surface pressure of only 6.1 millibars (0.087 psi).
The density of the Martian atmosphere decreases with altitude, resulting in less air resistance for projectiles as they ascend.
Experimental Setup and Measurements
To measure the trajectory of a projectile on Mars, an experiment could involve launching a projectile upward using a compressed air launcher.
The experiment would require equipment such as:
- Projectile launcher
- Measuring devices (e.g., high-speed camera, laser rangefinder)
- Data acquisition system
Data Analysis and Interpretation
The data collected from the experiment can be analyzed to determine the trajectory of the projectile. This includes calculating its height, velocity, and acceleration.
The experimental results can be compared to theoretical predictions of projectile motion on Mars, based on the Martian gravitational constant and atmospheric conditions.
Applications and Implications
Understanding projectile motion on Mars is important for designing rockets and spacecraft for Mars missions.
The results of the experiment can provide insights into the physics of Mars and its atmosphere, including the role of air resistance and wind.
Further research could explore the effects of different projectile shapes and sizes on their trajectories on Mars.
FAQ Explained
What factors influence the trajectory of a projectile on Mars?
Gravity, atmospheric density, wind patterns, and the initial velocity of the projectile.
How does the Martian atmosphere affect the trajectory of a projectile?
The Martian atmosphere exerts air resistance and wind forces, which can alter the projectile’s path and trajectory.
What are the potential applications of understanding projectile motion on Mars?
Designing rockets and spacecraft for Mars missions, understanding the Martian atmosphere, and advancing our knowledge of planetary dynamics.