Embark on an exciting journey through Unit 7 FRQ AP Human Geography, where we delve into the captivating world of human population growth, urbanization, economic development, political geography, and cultural geography. Prepare to be intrigued as we explore the intricate factors that shape our planet and its inhabitants.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with a thorough understanding of the demographic transition model, the forces driving population change, and the diverse urban landscapes that define our modern world. We’ll examine the complexities of economic growth, the nuances of political systems, and the rich tapestry of cultures that make our planet a vibrant and dynamic place.
Human Population Growth
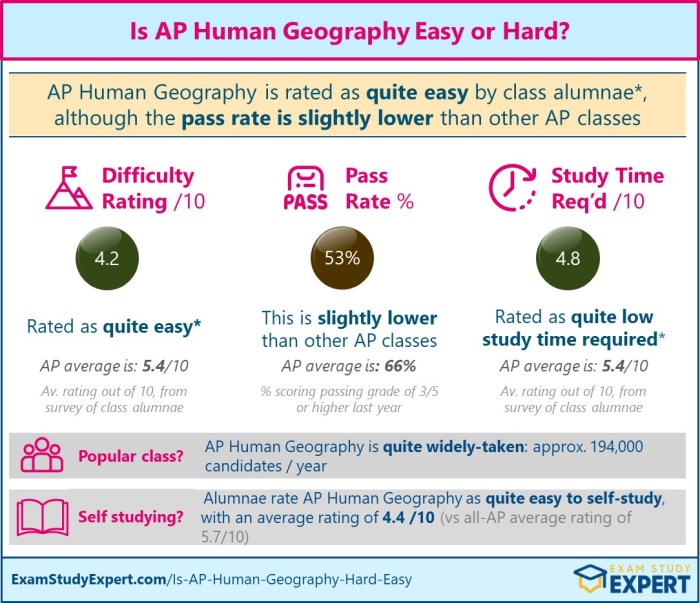
The human population has grown significantly over the centuries, and this growth has had a profound impact on the planet. The demographic transition model is a framework that helps us understand the different stages of population growth and decline.
Stages of the Demographic Transition Model
The demographic transition model has four stages:
- Pre-industrial stage:This stage is characterized by high birth rates and high death rates, resulting in a relatively stable population size.
- Transitional stage:This stage is characterized by a decline in death rates, while birth rates remain high, leading to a rapid increase in population size.
- Industrial stage:This stage is characterized by a decline in both birth rates and death rates, leading to a slower rate of population growth.
- Post-industrial stage:This stage is characterized by low birth rates and low death rates, resulting in a relatively stable population size.
Factors Influencing Population Growth and Decline
There are a number of factors that can influence population growth and decline, including:
- Economic factors:Economic development can lead to a decline in fertility rates, as people have fewer children in order to focus on their careers and education.
- Social factors:Social norms and values can also influence fertility rates. For example, in some cultures, it is considered important to have a large family, while in other cultures, it is considered more important to have a smaller family.
- Political factors:Government policies can also influence population growth and decline. For example, some governments have implemented policies to encourage population growth, while others have implemented policies to discourage population growth.
- Environmental factors:Environmental factors, such as food shortages and natural disasters, can also lead to a decline in population growth.
Examples of Countries at Different Stages of the Demographic Transition
Different countries are at different stages of the demographic transition model. For example, many developing countries are in the transitional stage, while many developed countries are in the post-industrial stage.
- Developing countries:Many developing countries, such as India and China, are in the transitional stage of the demographic transition model. These countries are experiencing a decline in death rates, but birth rates remain high, leading to a rapid increase in population size.
- Developed countries:Many developed countries, such as the United States and Japan, are in the post-industrial stage of the demographic transition model. These countries are experiencing low birth rates and low death rates, resulting in a relatively stable population size.
Urbanization
Urbanization is the process by which a growing population shifts from rural to urban areas. This shift is caused by several factors, including the desire for better economic opportunities, access to education and healthcare, and improved living conditions.
As we delve into the intricacies of unit 7 FRQ AP Human Geography, it’s essential to note the importance of foundational knowledge. For those seeking guidance on hunter education, hunter ed unit 6 quiz answers offers valuable insights. By reinforcing our understanding of these core concepts, we can confidently tackle the challenges posed by unit 7 FRQ AP Human Geography.
Urbanization has a number of consequences, both positive and negative. On the positive side, urbanization can lead to increased economic growth, innovation, and cultural diversity. On the negative side, urbanization can also lead to increased pollution, crime, and social inequality.
Types of Urban Areas
There are a number of different types of urban areas, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most common types of urban areas include:
- Metropolitan areas: These are the largest and most populous type of urban area. They typically consist of a central city and a surrounding area of suburbs.
- Micropolitan areas: These are smaller than metropolitan areas, but they still have a significant population and economy.
- Towns: These are smaller than micropolitan areas, and they typically have a population of less than 50,000 people.
- Villages: These are the smallest type of urban area, and they typically have a population of less than 10,000 people.
Major Urban Areas
Some of the major urban areas around the world include:
- Tokyo, Japan: The largest metropolitan area in the world, with a population of over 37 million people.
- New York City, United States: The largest metropolitan area in the United States, with a population of over 20 million people.
- London, United Kingdom: The largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of over 8 million people.
- Paris, France: The largest metropolitan area in France, with a population of over 12 million people.
- Mumbai, India: The largest metropolitan area in India, with a population of over 20 million people.
Economic Development
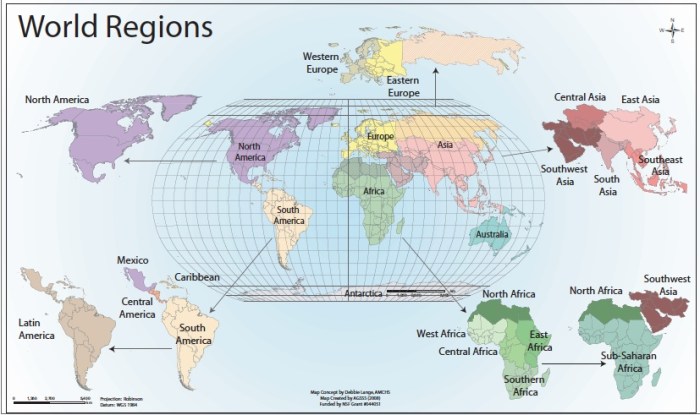
Economic development encompasses the processes by which countries improve their economic well-being. Various measures quantify this progress, including gross domestic product (GDP), gross national income (GNI), and the Human Development Index (HDI).
Factors Contributing to Economic Growth
Economic growth is driven by factors such as:
- Capital accumulation: Investments in infrastructure, technology, and human capital enhance productivity.
- Technological progress: Innovation and technological advancements increase efficiency and output.
- Human capital development: Education, healthcare, and skills training improve the workforce’s productivity.
- Natural resources: Abundant natural resources can contribute to economic growth, particularly in resource-dependent economies.
- Government policies: Favorable policies, such as stable economic conditions, can foster investment and growth.
Examples of Countries at Different Levels of Economic Development
Countries exhibit varying levels of economic development, ranging from:
- Least developed countries (LDCs): Characterized by low GDP, limited infrastructure, and high poverty rates (e.g., Niger, Afghanistan).
- Developing countries: Experiencing rapid economic growth and urbanization, with improving living standards (e.g., China, India).
- Developed countries: Highly industrialized economies with high GDP, advanced technology, and strong infrastructure (e.g., United States, Japan).
Political Geography
Political geography examines the relationship between political phenomena and the Earth’s surface. It encompasses the study of political boundaries, territorial organization, and the distribution of political power.
Types of Political Systems, Unit 7 frq ap human geography
Political systems vary widely around the world. Some common types include:
- Democracy:A system where power is vested in the people and exercised through a system of representation.
- Autocracy:A system where power is concentrated in a single person or a small group.
- Oligarchy:A system where power is held by a small elite group.
- Theocracy:A system where political power is derived from religious authority.
Examples of Political Systems
Examples of political systems around the world include:
- United States:A representative democracy
- China:A one-party socialist state
- Russia:A semi-presidential republic
- Saudi Arabia:An absolute monarchy
- Vatican City:A theocratic city-state
Cultural Geography

Cultural geography examines the spatial distribution and interaction of human cultures. It explores how cultural traits, beliefs, values, and practices shape the landscape and are influenced by it.
Elements of Culture
Culture encompasses various elements that define a group’s identity and way of life:
- Material Culture:Physical objects, artifacts, and technologies created by a culture.
- Non-Material Culture:Beliefs, values, norms, and practices that guide a culture’s behavior.
- Language:A system of communication that reflects a culture’s unique perspective and experiences.
- Religion:Beliefs and practices related to the supernatural or spiritual realm.
- Arts:Creative expressions, including music, dance, painting, and literature, that convey a culture’s emotions and experiences.
Examples of Different Cultures
The world is home to a vast array of cultures, each with its distinct characteristics:
- Western Culture:Characterized by individualism, rationalism, and a focus on science and technology.
- Eastern Culture:Emphasizes collectivism, harmony with nature, and spiritualism.
- Islamic Culture:Rooted in the teachings of Islam, it values community, modesty, and hospitality.
- Indigenous Cultures:Represent the unique traditions and practices of indigenous communities around the world.
Questions Often Asked: Unit 7 Frq Ap Human Geography
What are the key stages of the demographic transition model?
The demographic transition model Artikels four main stages: pre-industrial, transitional, industrial, and post-industrial.
What factors influence population growth and decline?
Population growth and decline are influenced by factors such as birth rates, death rates, migration, and environmental conditions.
What are the different types of urban areas?
Urban areas can be classified into various types, including cities, towns, suburbs, and metropolitan areas.
What are the key measures of economic development?
Common measures of economic development include GDP per capita, literacy rates, and life expectancy.
What are the different elements of culture?
Culture encompasses a wide range of elements, including language, religion, values, beliefs, customs, and traditions.